Flux LoRA Dataset Preparation: Complete Guide to Training Data (2025)
Master Flux LoRA dataset preparation with this comprehensive guide. Learn image selection, captioning strategies, data augmentation, and best practices for training high-quality custom models.

Your Flux LoRA is only as good as your training data. A carefully prepared dataset of 15 images can outperform a sloppy collection of 100. This guide covers everything you need to know about creating the perfect training dataset.
Quick Answer: Flux LoRA datasets need 10-30 high-quality images at 1024x1024 minimum resolution. Each image requires detailed captions with a consistent trigger word. Variety in poses, lighting, and backgrounds prevents overfitting. Caption quality matters more than image quantity. Use BLIP or Florence-2 for base captions, then manually refine them.
- Image count: 10-30 images (quality over quantity)
- Resolution: 1024x1024 minimum
- Format: PNG or high-quality JPEG
- Captions: Detailed, consistent trigger word
- Variety: Different poses, lighting, backgrounds
Why Dataset Quality Matters
I've trained hundreds of LoRAs over the past few years, and the single biggest predictor of success is dataset quality. You can have the perfect training configuration, optimal hardware, and infinite patience, but if your training images are inconsistent or poorly captioned, you'll get mediocre results. Conversely, a well-curated dataset of just 15 carefully selected images can produce a LoRA that captures your concept with remarkable fidelity.
This isn't just about technical quality like resolution and sharpness, although those matter too. It's about what you're teaching the model. Every image in your dataset is a lesson, and every inconsistency is a contradictory lesson that confuses the learning process. Think of it like teaching a language: clear, consistent examples teach faster than a mix of correct and incorrect usage.
The Quality Multiplier
Dataset quality has an exponential effect on LoRA quality:
| Dataset Quality | Training Outcome |
|---|---|
| Excellent (10 images) | Excellent LoRA |
| Good (30 images) | Good LoRA |
| Poor (100 images) | Poor LoRA |
More images with problems just train more problems into your model.
Common Dataset Mistakes
Quantity over quality: Many beginners collect 100+ images without curation. This introduces inconsistencies that confuse training.
Inconsistent subjects: Training a person LoRA with images from different ages, hairstyles, or with makeup variations creates blurry, inconsistent outputs.
Poor captions: Generic captions like "a woman" don't teach the model what makes your subject unique.
No variety: All images with same pose, lighting, and background causes severe overfitting.
Image Selection Criteria
Technical Requirements
Resolution:
- Minimum: 1024x1024 pixels
- Recommended: 1536x1536 or higher
- Flux works best with high-resolution training data
Quality:
- Sharp, in-focus images
- No motion blur
- No compression artifacts
- No watermarks or text overlays
- Proper exposure (not too dark/bright)
Format:
- PNG preferred (lossless)
- High-quality JPEG acceptable (90%+ quality)
- Avoid heavily compressed images
Content Requirements
Subject consistency: For subject LoRAs, ensure the subject is truly consistent:
- Same person (not lookalikes)
- Consistent age/appearance
- Same character design (for fictional)
Subject visibility:
- Face clearly visible (for portraits)
- Subject should be prominent in frame
- Avoid heavily cropped or obscured subjects
Variety within consistency: Balance is key. Include:
- Different angles (front, 3/4, side)
- Various expressions (neutral, smile, serious)
- Multiple lighting conditions
- Different backgrounds
- Various outfits/clothing
Dataset Size Guidelines
Optimal Counts by LoRA Type
Subject/Person LoRA:
- Minimum: 10 images
- Recommended: 15-25 images
- Maximum useful: 30-40 images
Beyond 40 images, quality plateaus and training time increases without benefit.
Style LoRA:
- Minimum: 15 images
- Recommended: 30-50 images
- More images help capture style nuances
Concept/Object LoRA:
- Minimum: 8 images
- Recommended: 15-20 images
- Show object from multiple angles
Quality Tiers
Tier 1: Essential (Core Set) 10-15 images that perfectly represent your subject. These are your best, most clear, most representative images.
Tier 2: Supporting 10-15 additional images adding variety. Different conditions, angles, contexts.
Tier 3: Edge Cases 5-10 images showing unusual angles or conditions. Optional, helps generalization.
Image Preparation Workflow
Step 1: Collection
Gather 2-3x more images than you need. You'll curate down from this pool.
For subject LoRAs:
- Professional photos if available
- Multiple photo sessions
- Screenshots from video (be selective)
- AI upscaled images (if starting low-res)
For style LoRAs:
- Official artwork from the style
- Consistent examples of the aesthetic
- Avoid mixing artists/periods
Step 2: Initial Curation
Eliminate images with:
- Blur or motion artifacts
- Poor lighting or exposure
- Occluded subjects
- Inconsistent appearances
- Watermarks or overlays
- Duplicate or near-duplicate poses
Step 3: Cropping and Resizing
Cropping guidelines:
- Subject should fill 60-80% of frame
- Include some context/background
- Consistent framing across dataset
- Square crops work best for Flux
Resizing: ```bash
ImageMagick batch resize to 1024x1024
mogrify -resize 1024x1024^ -gravity center -extent 1024x1024 *.png ```
Step 4: Quality Enhancement (Optional)
For lower quality source images:
- AI upscaling (Real-ESRGAN)
- Noise reduction
- Color correction
- Sharpening (subtle)
Don't over-process. The goal is clarity, not artificial enhancement.
Step 5: Final Selection
From your curated pool, select final images ensuring:
- At least 2-3 front-facing views
- At least 2-3 side/3/4 views
- Variety in lighting (indoor, outdoor, studio)
- Variety in expression
- Variety in background
- No redundant poses
Captioning Strategies
 Automated captioning tools provide a starting point that you refine with manual adjustments.
Automated captioning tools provide a starting point that you refine with manual adjustments.
Caption Structure
Every caption should follow this pattern: ``` [trigger word], [subject description], [action/pose], [clothing], [setting], [lighting], [style/quality] ```
Example Captions
Subject LoRA (person "alexphoto"): ``` alexphoto, young woman with long brown hair and green eyes, smiling warmly at camera, wearing casual blue sweater, in modern coffee shop, soft natural window lighting, professional photography, sharp focus ```
Free ComfyUI Workflows
Find free, open-source ComfyUI workflows for techniques in this article. Open source is strong.
Style LoRA ("oilpaint style"): ``` oilpaint style, portrait of elderly man with weathered face, contemplative expression looking to the side, wearing dark formal attire, against muted brown background, dramatic chiaroscuro lighting, visible brushstrokes, impasto technique, classical composition ```
Trigger Word Selection
Good trigger words:
- Unique: "alexphoto" not "woman"
- Memorable: Easy to type consistently
- Unused: Not a common word in training data
- Simple: Avoid special characters
Examples:
- For person: firstname + identifier (sarahmodel, jakeshot)
- For style: stylename + style (oilpaint style, animex style)
- For concept: conceptname + type (firemagic effect, gotharch building)
Automated Captioning Tools
BLIP-2: Good starting point, generates basic descriptions. ```bash
Using Python
from transformers import Blip2Processor, Blip2ForConditionalGeneration
Process images and generate captions
```
Florence-2: More detailed, better for complex scenes.
WD Tagger: Excellent for anime/illustration style content.
Recommended workflow:
- Generate base captions with BLIP-2 or Florence-2
- Add trigger word to beginning of each
- Manually review and enhance each caption
- Add missing details (lighting, quality, style)
- Ensure consistency across captions
Caption Best Practices
Do:
- Use consistent terminology throughout dataset
- Describe what makes each image unique
- Include technical photography terms
- Mention distinguishing features
- Keep trigger word position consistent (usually first)
Don't:
- Use subjective terms ("beautiful", "amazing")
- Copy-paste identical captions
- Ignore important visual details
- Contradict what's shown in image
- Use ambiguous descriptions
Data Augmentation
When to Augment
Data augmentation artificially increases dataset size. Consider it when:
- Dataset is smaller than 10 images
- Training shows overfitting
- You need more variety
Safe Augmentation Methods
Horizontal flipping: Creates mirror versions. Safe for most subjects. ```python from PIL import Image img_flipped = img.transpose(Image.FLIP_LEFT_RIGHT) ``` Note: Update captions if direction matters ("looking left" becomes "looking right").
Slight rotation: ±5 degrees adds variety without distortion.
Color jittering: Subtle brightness/contrast changes simulate lighting variation.
Cropping variations: Different crops of same image showing different framings.
Want to skip the complexity? Apatero gives you professional AI results instantly with no technical setup required.
Augmentation to Avoid
Heavy rotation: Distorts natural appearance Aggressive color changes: Creates unrealistic images Stretching/scaling: Distorts proportions Noise addition: Reduces quality signals
Augmentation Tools
Albumentations (Python): ```python import albumentations as A
transform = A.Compose([ A.HorizontalFlip(p=0.5), A.RandomBrightnessContrast(p=0.2), A.Rotate(limit=5, p=0.3), ]) ```
ImageMagick (CLI): ```bash
Flip horizontal
convert input.png -flop output_flipped.png
Rotate 5 degrees
convert input.png -rotate 5 output_rotated.png ```
Dataset Organization
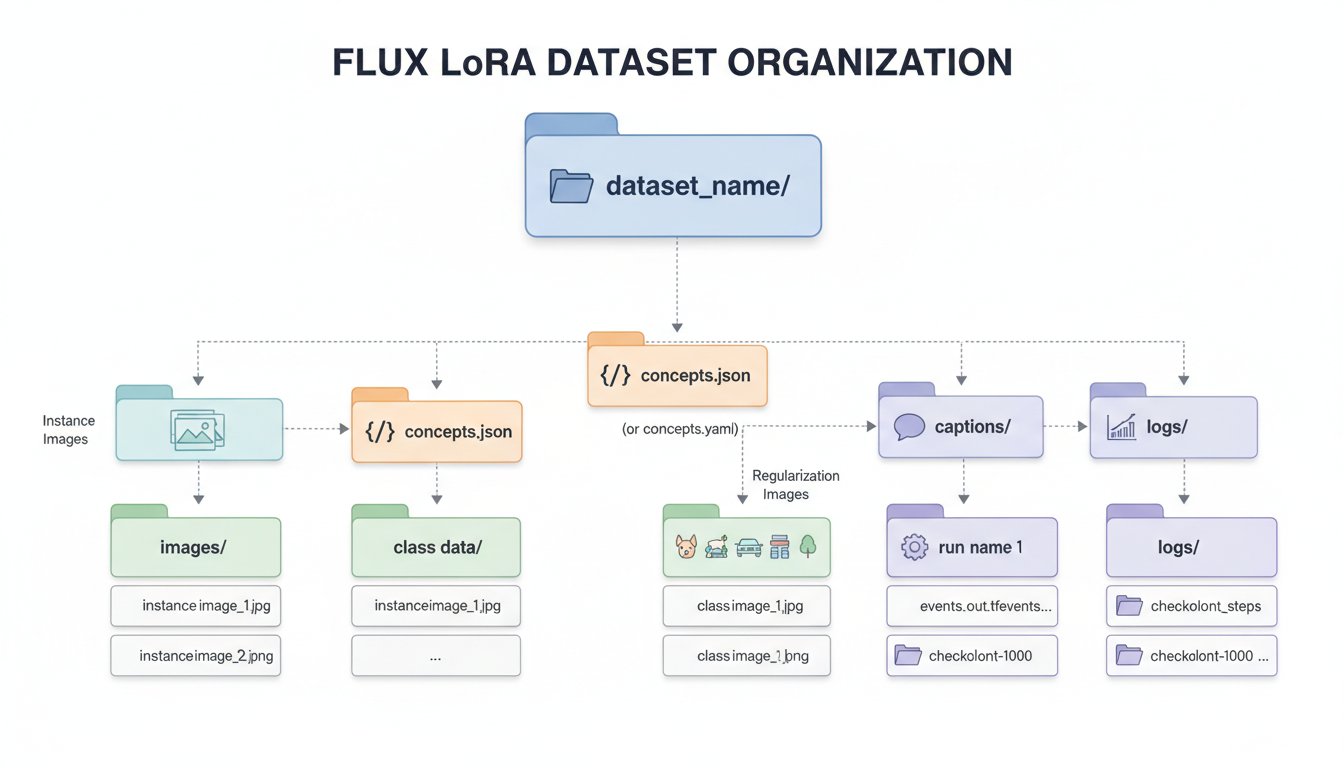 Proper folder organization keeps your training data organized and compatible with different training tools.
Proper folder organization keeps your training data organized and compatible with different training tools.
Folder Structure
``` dataset/ ├── images/ │ ├── 001.png │ ├── 002.png │ └── ... ├── captions/ │ ├── 001.txt │ ├── 002.txt │ └── ... └── metadata.json ```
Or combined format: ``` dataset/ ├── 001.png ├── 001.txt ├── 002.png ├── 002.txt └── ... ```
Naming Conventions
Keep names simple and matched:
- image_001.png → image_001.txt
- portrait_front.png → portrait_front.txt
Avoid:
- Spaces in filenames
- Special characters
- Very long names
Validation Checklist
Before training, verify:
- All images have matching caption files
- Trigger word appears in every caption
- Images are correct resolution
- No corrupted files
- Captions are properly encoded (UTF-8)
- File extensions are lowercase and consistent
Advanced Techniques
Regularization Images
For subject LoRAs, regularization images prevent the model from forgetting general concepts.
What they are: Images of similar but different subjects. For a person LoRA, use photos of other people.
Purpose: Prevents LoRA from modifying the base model's understanding of the general category.
Join 115 other course members
Create Your First Mega-Realistic AI Influencer in 51 Lessons
Create ultra-realistic AI influencers with lifelike skin details, professional selfies, and complex scenes. Get two complete courses in one bundle. ComfyUI Foundation to master the tech, and Fanvue Creator Academy to learn how to market yourself as an AI creator.
Implementation: ``` dataset/ ├── subject/ (your actual training images) │ ├── alex_001.png │ └── ... └── regularization/ (generic similar images) ├── person_001.png └── ... ```
Caption regularization images with generic descriptions (no trigger word): "photograph of a woman, professional lighting, high quality"
Multi-Concept Datasets
Training multiple concepts in one LoRA:
``` dataset/ ├── concept_a/ │ ├── a_001.png (caption: "concepta, ...") │ └── ... ├── concept_b/ │ ├── b_001.png (caption: "conceptb, ...") │ └── ... ```
Use different trigger words for each concept.
Quality Weighting
Some trainers support image weighting. Mark your best images for higher influence:
``` 001.png # weight: 1.5 (best example) 002.png # weight: 1.0 (standard) 003.png # weight: 0.8 (acceptable but not ideal) ```
Platform-Specific Requirements
Kohya SS Requirements
``` dataset/ └── 10_subjectname/ (number = repeats) ├── image1.png ├── image1.txt └── ... ```
Folder naming: [repeats]_[concept name]
SimpleTuner Requirements
``` dataset/ ├── images/ └── captions/ ```
Separate folders for images and captions with matching names.
ai-toolkit Requirements
Supports multiple formats. JSON metadata often preferred: ```json { "images": [ {"path": "001.png", "caption": "trigger, description..."}, {"path": "002.png", "caption": "trigger, description..."} ] } ```
Common Problems and Solutions
Problem: LoRA Not Learning Subject
Symptoms: Output looks nothing like training images.
Solutions:
- Check trigger word is in all captions
- Verify images actually match each other
- Increase training steps
- Review caption quality
Problem: Overfitting
Symptoms: Only reproduces exact training poses, can't generalize.
Solutions:
- Add more variety to dataset
- Reduce training steps
- Use regularization images
- Increase dataset size with diverse images
Problem: Inconsistent Results
Symptoms: Sometimes works, sometimes doesn't.
Solutions:
- Improve caption consistency
- Remove contradictory images
- Standardize image quality
- Check for duplicate/near-duplicate images
Problem: Style Not Transferring
Symptoms: Style elements missing from outputs.
Solutions:
- Add more style-specific descriptions in captions
- Include more examples of the style
- Be more explicit about style characteristics
- Consider separate style and content descriptions
Quality Assurance Workflow
Pre-Training Checklist
- Visual review: Open all images in gallery view, look for outliers
- Caption review: Read through all captions, check consistency
- Technical check: Verify resolutions, formats, file integrity
- Trigger word check: Confirm trigger appears consistently
- Variety check: Ensure sufficient pose/lighting variation
Test Training
Before full training:
- Train for 10% of planned steps
- Generate test images with trigger word
- Evaluate if concept is emerging
- Adjust dataset if needed
Iterative Refinement
After initial training:
- Identify weak areas in generation
- Add images addressing those weaknesses
- Retrain with improved dataset
- Repeat until satisfied
Tools and Resources
Captioning Tools
| Tool | Best For | Automation Level |
|---|---|---|
| BLIP-2 | General images | High |
| Florence-2 | Detailed scenes | High |
| WD Tagger | Anime/illustration | High |
| Manual | Final refinement | None |
Image Processing Tools
| Tool | Use Case |
|---|---|
| ImageMagick | Batch resize/crop |
| GIMP | Manual editing |
| Real-ESRGAN | Upscaling |
| Topaz | Enhancement |
Dataset Management
| Tool | Features |
|---|---|
| Birme | Web-based batch crop |
| XnConvert | Batch processing |
| Custom scripts | Full control |
Frequently Asked Questions
How many images do I really need?
For subjects: 15-25 quality images outperform 100 poor ones. Quality and variety matter more than quantity.
Should I include bad examples?
No. Only include images representing what you want to generate. Bad examples train bad patterns.
Can I mix photo and artwork?
Not recommended for subject LoRAs. Style mixing causes confusion. For style LoRAs, stay consistent within style.
How long should captions be?
50-150 words per caption is typical. Enough detail to describe the image, not so much it becomes noise.
Do I need professional photos?
Not necessarily. Phone photos work if they're sharp, well-lit, and high resolution. Quality matters more than equipment.
Should every caption be unique?
Mostly yes. Each caption should accurately describe its specific image. Some elements will repeat (trigger word, consistent subject features).
How do I caption images with the subject doing nothing?
Describe the pose, expression, and passive state: "standing relaxed, neutral expression, arms at sides, looking at camera"
Can I use AI-generated images in the dataset?
For style LoRAs, possibly. For subject LoRAs, risky since AI images may not accurately represent real subjects. Use with caution.
What if my subject has changed appearance?
Create separate datasets for different appearances, or choose one appearance period for consistency. Mixing confuses training.
How do I handle group photos?
Crop to isolate your subject. Only include group shots if the subject is clearly prominent and identifiable.
Wrapping Up
Dataset preparation is where LoRA quality is won or lost. Time invested here pays dividends in training results.
Key takeaways:
- 15-25 high-quality images beat 100 mediocre ones
- Consistent trigger words in detailed captions
- Variety in poses, lighting, backgrounds
- Automated captioning + manual refinement
- Validate everything before training
With a well-prepared dataset, your Flux LoRA will consistently produce the results you want.
For training workflow, see our ultimate LoRA training guide. For video LoRA training, check LTX-2 LoRA training. Generate AI images at Apatero.com.
Ready to Create Your AI Influencer?
Join 115 students mastering ComfyUI and AI influencer marketing in our complete 51-lesson course.
.png)
